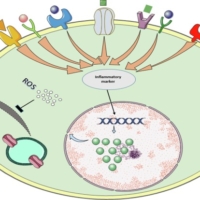
Best Practices for Anxiety Treatment | Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
this episode was pre-recorded
as part of a live continuing education webinar on-demand CEUs are
still available for this presentation AllCEUs.com/Anxiety-CEU I’d like to welcome everybody to today’s
presentation on best practices for the treatment of anxiety I am your host, Dr. Dawn Elise Snipes now not too long ago we did
a presentation on strengths-based biopsychosocial approaches to addressing anxiety while
those are wonderful you know I thought maybe we ought to look at you know what’s some of the
current research so I went into PubMed which is I don’t know it’s playground for me it’s where
you find a lot of the journal articles and you can sort and I sorted by articles that were
done and meta-analyses that were done within the past five years so that gives us an idea
about current research I mean there’s a lot of stuff that is still the same like some of
the medications that were known to work ten years ago are still known to be you know good
first-line treatments but there are also some newcomers that we’ll talk about and there are
also some changes that we’re going to talk about so we’re going to explore some common causes
for anxiety symptoms in order to treat it we really need to and of course this does play into
the biopsychosocial aspect we really need to understand kind of what causes it because anxiety
that’s caused by for example somebody having a racing heart may be different than anxiety that’s
caused for somebody who has abandonment issues so we’re gonna treat the two things differently so
we want to look at some of the common causes we’re gonna look at some common triggers for anxiety
you know what are some of these common themes that we see in practice and I will ask you to share
some of the themes that you see that underline or underlie a lot of your clients anxiety and
identify current best practices for anxiety management including counseling interventions
medications physical interventions and supportive treatments so we care because anxiety can
be debilitating and a lot of our clients have anxiety a lot of our clients have anxiety
comorbid with depression and they’re looking at us going how can I feel anxious and stressed out
and like I can’t sit still and depressed at the same time you know when you’re depressed you’re
supposed to want to sleep well a lot of times people who are have both issues really want to
sleep but they can’t so I want to help clients understand that also sometimes anxiety when
people are anxious for long enough the body starts kind of holding on to the cortisol the body
actually recognizes at a certain point this is a losing battle I’m not going to put energy into
this anymore so it starts with drawing some of its excitatory neurotransmitter so to speak and
people will start to feel depressed basically the brain has already said this is hopeless this is
you’re you’re helpless to change the situation so then people start feeling hopeless and helpless
which is sort of the definition if you will of depression low-grade chronic stress and anxiety
arose energy and people’s ability to concentrate so if we’re going to help them become their uber
selves we need to help them figure out how to address anxiety not just generalized overwhelming
debilitating anxiety but also panic social anxiety and those minor anxiety triggers that come along
that may not meet the threshold for a diagnosis anxiety is a major trigger for addiction relapse
if you have a client who is self medicated before or had an addiction for some reason anxiety is a
major trigger increased physical pain when anxiety goes up people tend to tense their muscles when
they tense their muscles they tend to feel more pain I mean think about when you’re stressed you
tend to have more pain like in your neck in your back and things that already hurt may hurt more
why because serotonin which is one of our major anti-anxiety neurotransmitters is also one of our
major pain modulators so when serotonin levels are too low because anxiety is high then our pain
perception is going to be more acute and people can have sleep problems if you’re stressed out
your body thinks there’s a threat you’re not going to be able to get into that deep restful
sleep you may have you may sleep you may sleep a lot but it’s probably not quality sleep which
means your neurotransmitters may get out of whack your hormones make it out of whack and your body
is going to start perceiving your itself in a persistent state of stress when we’re exhausted
the body knows that we may be the weakest link in the herd so it continues to secrete cortisol
to keep keep you on alert a little bit so you may again you may be resting kind of like when
you have a new baby at home those first couple of months that my children were home from the
hospital I slept but I didn’t sleep well I mean the slightest little noise and I was awake and I
was looking around and you know I felt it I felt exhausted and a lot of new parents do so triggers
for anxiety abandonment and rejection and we’re going to talk about ways we might want to deal
with these things but some of the underlying themes that I’ve seen in a lot of clients and when
I do the research what a lot of what themes that come out include low self-esteem if someone has
low self-esteem they’re looking to be externally validated oftentimes they’re looking for somebody
else to tell them you’re lovable you’re okay so that can lead to anxiety about not having
people to tell them you’re okay which makes their relationships tenuous and can make them
dysfunctional irrational thoughts and cognitive distortions may lead people to believe that if I’m
not perfect for example I am not lovable so we’re going to look at some irrational thoughts and
cognitive distortions unhealthy social supports and relationships when you’re in a relationship
it takes two to tango and even if your client is relatively mentally and physically healthy if they
are in a dysfunctional relationship they can fear abandonment and rejection if that other person
is always saying if you don’t do X I’m going to leave you or if that other person is always
cheating on them or whatever so relationships can trigger abandonment anxiety and ineffective
interpersonal skills can lead to relationship turmoil and social exile if our clients are in
relationships even if they’re not completely dysfunctional if our clients are not able to ask
for what they need and set appropriate boundaries and manage conflict effectively because conflict
happens in every relationship then they may start to argue more which may lead to fearing may lead
to relationships ending in the past and them going well every relationship I get into ends which
means I must not be lovable so they start fearing abandonment and rejection so these are four areas
that we can look at one more assessing clients another issue is the unknown and loss of control
a lot of times negative self-talk and cognitive distortions can contribute to that if I don’t have
control of everything then it’s all going to be a disaster negative others when clients hang out
or when people hang out with negative people it kind of wears on you after a while you notice
that people who are tend to be more negative pessimistic conspiracy minded tend to hang out
with people who are also negative pessimistic and conspiracy minded so if you’re hanging out with
somebody who tends to be anxious then the anxiety can be palpable and it can kind of permeate
physical complaints can lead people to be anxious because they don’t know what’s causing it
like I said earlier sometimes if your heart starts to race if you don’t know what’s causing it you
can start thinking I’m having a heart attack or I’m gonna die when people have panic attacks for
example they truly think they’re having a heart attack and it’s I’ve had them they are very
very unpleasant experiences but when people start having physical complaints and it can be you
know they have a weird rash that they can’t get to go away or it whatever but when they don’t know
what it is and they can’t control it they can’t make it go away they start thinking about all
the worst-case scenarios and going online and getting on WebMD which usually gives you all the
worst-case scenarios um so physical complaints are important we need to normalize the fact that
nobody’s pain-free all the time and you know the fact that you may have an ache or a pain or a lump
or a bump or you know a cough most likely you know when we look at probability the probability of it
being something significant is pretty small now do you want to get it checked out probably but
you know the probability that is anything to be worried about is is relatively small and a sense
of powerlessness can trigger fear of the unknown and loss of control for somebody who doesn’t
feel like they have any agency in their life if they have an external locus of control or
if they felt victimized all of their life then they may fear not being in control they may be
holding on and saying okay this is the one area of my life I can control when I grew up you know
I grew up in a very chaotic environment I had no control I was bounced around in the foster system
yadda yadda yadda now that I’m an adult you know I can control these things and I am going to hold
on with white knuckles and if I can’t control everything then that terrifies me death and
loss are other triggers for anxiety and it can be people or pets and pets are important I don’t
want to minimize pets because you know they are little parts of a lot of our families so making
sure we check that my daughter’s dog for example is it’s getting old she’s getting older she’s 14
now I think and you know she’s in decent health we took her to the vet and the vet said yeah she’s
got a little heart murmur but that’s expected for a 14 year old dog and but when she goes out if she
doesn’t come back when I call her I have this rush of anxiety for a second oh my gosh I hope this
wasn’t the day so anxious around losing people and you know if she when she crosses the bridge
she will and and you know I’m okay with that I’m I have a harder time dealing with my daughter’s
emotional turmoil when that happens and because she’s grown up with this dog so you know those
are the types of things that we want to talk about with our clients what things are weighing on you
that you may not even be thinking about because I know in the back of my mind there’s always that
worry about one of our donkeys and her dog jobs and promotions can trigger anxiety if people are
afraid they’re gonna lose their job if they’re always afraid that you know they’re gonna walk in
and get a pink slip or get fired you know we want to help them look at how realistic is that are
you doing what you need to do in order to achieve and keep your job and sometimes it’s not easy to
answer I mean the first thought that a lot of us have is well you know if you’re doing the right
thing so just do it but there are those bosses out there and I’ve had some really amazing bosses
a lot of them and I’ve had two really horrendous bosses and those two bosses I could never I
never felt like I was able to do anything right and so going to those jobs there was always this
anxiety about what I’m what am I going to get in trouble for today so you want to talk with people
about does your job cause anxiety what can you do to moderate that anxiety the same thing with
promotions people may get anxious about whether they’re going to get promoted safety and security
you know when you lose safety and security you can feel really anxious so if there’s a break-in at
the house next door or a shooting down the road or you start watching the news you can feel very
unsafe and unsecure really quickly so we want to help people figure out how safe and secure are you
really and a lot of it goes back to really looking at facts when people lose their dreams and hopes
or fear that they’re going to lose their dreams and hopes they can start to get anxious you know
they have this dream that they’re going to be a doctor or I just finished the presentation on
helping high school students transition to college and a lot of high school students for example
start college with these wide eyes and hopes to save the world and they want to be doctors
and engineers and this and that and they get into it and they realize that it’s a lot harder
than they thought or they realize that you know what I really don’t like this but I’ve already
committed to it so what do I do or I want to help people but I can’t I can’t cut it doing this you
know for me I figured out in my second year that I wasn’t going to medical school because I wasn’t
going to pass calculus and that caused a lot of anxiety it was like okay what am I gonna do now
you know what career should I choose so helping people figure out do you have dreams that have
maybe kind of crashed and burned and you have to find new ones you know okay that one we’ve got to
accept it figure out that it’s not going to be and what can you do now people may also have dreams
about relationships they get into relationships and they see themselves with this person forever
and then this relationship ends and or starts to get rocky and they’re like but that’s my dream
what happens if my that’s got to happen because it’s my dream I don’t know how to function if
that goes away we want to help people be able to rewrite their narrative and then sickness spiders
and other phobias kind of goes in with death a lot of times when people get sick they start getting
anxious that oh my gosh what if this is terminal oh my gosh what if this is you know incurable
if I get bit by a spider it’s gonna kill me and which is rare you know there are very few spiders
that are actually that poisonous same thing with snakes going over bridges I’ve shared with you all
that is not one of my irrational fears you know I am just terrified that you know something’s going
to happen and I’m going to get pushed off the side of the bridge which is completely irrational but
we need to help people look at those and identify the thoughts that they’re telling themself about
those phobias and deal with that anxiety failure is another trigger for anxiety especially in
this culture our culture American culture in large part puts a high premium on success
and perfectionism so when people realize that they’re not perfect they may start to get anxious
because they feel like if I’m not perfect then I’m a failure you know those cognitive distortions of
all-or-nothing thinking and they start with that negative self-talk you know you can’t do anything
right so those are some of the issues that you know we often see in counseling sessions so what
do we do you know somebody comes in and is like I can’t live this way with anxiety depression and
substance disorders as well as a range of physical disorders are often comorbid so this is the first
thing we need to realize we need to realize that we’re very rarely dealing with a very simple
diagnosis you know when somebody comes in we need to figure out you know if they come in and they’re
presenting with depression all right let’s talk about that and then we start realizing that their
depression started to occur after a long period of being really really anxious okay so we need
to deal with that but we also need to help them with their sense of hopelessness and helplessness
we need to develop that sense of empowerment and then substance disorders we know that substance
use is often a way of self-medicating but we also know that it monkeys with the neuro chemicals
in the brain and can contribute to anxiety and depression same thing with physical issues pain
from physical disorders anxiety about having physical disorders medications you’re taking for
physical disorders can all contribute to anxiety so we need to look at the person as whole and go
what are all the things that are contributing to the anxiety and what are all the things that the
anxiety is contributing to so we have we start having this big list of stuff that needs to be
addressed and then we can start figuring out okay where do we start so knowing that these things
are comorbid helps researchers explore pathways to mental disorders so they can start figuring
out you know what little string can we pull to unravel this blanket of anxiety so it doesn’t
suffocate somebody and for us as clinicians it provides us key opportunities to intervene you
know sometimes clients will come in and they’re start talking they start talking about their
anxiety and their their physical issues you know maybe their anxieties about you know heart
palpitations and because that’s a common one we may want to encourage them to go see the doctor to
get that ruled out you know rule out anything that has to do with hormone imbalances or you know
heart conditions or anything else that might be contributing to it which can help them address
it and if they do have physical disorders let’s go with hormone imbalances that are contributing
to the heart palpitations then they can start to treat that if they don’t start to treat that then
no amount of talk therapy we do is going to get them to the quality of life that they’re looking
for because they’re still gonna feel those so we want to make sure that we’re addressing them
holistically anxiety disorders should be treated with psychological therapy pharmaco therapy or a
combination of both and what they found and this is no surprise this is kind of old news is that
counseling Plus pharmacotherapy tends to have the best outcomes but separating the two they have
similar outcomes in many cases but that’s just looking at and I hate to call it simple anxiety
but we’re just looking at anxiety symptoms here we’re not looking at full quality of life and we
want to make sure that we’re also including any medical issues behavioral therapy is regarded
as the psychotherapy with the highest level of evidence there are a variety of cognitive
behavioral approaches ranging from acceptance and commitment therapy to dialectical behavior
therapy to CBT to rebt you know any of those that deal with the thoughts and the cognitions fall in
that realm and it has been found to be effective the current conceptualization of the etiology
of anxiety disorders includes an interaction of psychosocial factors such as childhood adversity
or stressful events and a genetic vulnerability so the psychosocial factors and these are other
things when we do our assessment we want to pay attention to because our approach for treatment
is going to be different for people for example who have trauma related brain changes maybe
then for somebody who doesn’t so we want to look at childhood adversity and stressful events
that it may have caused basically what I what I tell clients is like rewiring of the brain there
are trauma related brain changes in soldiers and especially in children or in people who’ve been
exposed to extreme trauma that are designed to protect them but it also can cause complications
kind of later on in dealing with anxiety coping skills that were learned that are ineffective you
know sometimes people grow up in a household or an environment or a situation where they don’t learn
effective coping skills so we need to kind of help them unlearn those and learn new ones build on
their strengths and trauma issues that may still need to be dealt with such as domestic violence
you know if they grew up a lot around a lot of domestic violence they may think you know I’m
out of that situation it’s over I don’t want to think about it it’s not bothering me anymore or a
parental absence and I put absence because it can be death it can be a parent that just packed up
and left it could be a child that got put up for adoption whatever put the child in a position of
feeling like they were rejected by a parent can be very traumatic and bullying among other things
but there are a lot of trauma issues that people once they’re out of that situation often say you
know I’m out of it it’s not a big deal I dealt with it let’s move on and they don’t realize the
full ramifications and how that’s contributing to their current anxiety and their current self talk
and cognitions current stressors if somebody has a lot of current stressors that’s also going to
impact whether they develop generalized anxiety you know we’re kind of stacking the deck here and
the current availability of social support if they don’t have effective current social support then
they’re gonna have difficulty bearing the weight of everything on their own shoulders so we want
to look at all these psychosocial factors when we do our assessment now going back to trauma
issues if you’ve taken the trauma courses at all CEUs you know that some people are not ready
to acknowledge that the trauma is still bothering them or work on the trauma and that’s okay we
can educate them that it might be an issue and then let them choose how to address it but
we want to bear in mind the fact that you know this could be sort of an underlying force
motivating some of the current cognitions and genetic vulnerability so you take any three
people and you put them or 300 people and you put them through roughly the same psychosocial
situations they’re all probably going to react a little bit differently based on their prior
experiences but also because of their genetic makeup there are certain permutations and they
found four we’ll talk about later that makes the brain more or less responsive to stress and
more or less responsive to serotonin which is your calming chemical so brains that are less
responsive to serotonin aren’t going to you know send out as much or send out serotonin as easily
so people can stay kind of tensed and wired that’s really oversimplified explanation but that’s
all you really need for right now so genetic vulnerability impacts people’s susceptibility
to the effects and development of dependence on certain substances which can increase anxiety
when people are detoxing from alcohol when they’re detoxing from benzos when they’re detoxing from
opiates they can feel high levels of anxiety when they take opiates some people find that opiates
have wonderful anti-anxiety properties not that I am advocating for the use of opiates I’m
just client experiences have shown that that can be true so some people are going to be
more susceptible to the anti-anxiety effects of certain substances and some people are going
to be Cerrone to become dependent on substances where others may not and that part of that is
genetic vulnerability and they estimates about 30% of the predictability of the development
of anxiety disorders is genetic and genetics also impact which medications are effective
if you have genetic makeup a then SSRIs might be helpful if you have genetic makeup be then
atypical antipsychotics may be a more effective and SSRIs might not do anything which is why
a lot of our clients get so frustrated because you know there’s no way to figure out exactly I
guess there is now that there’s genetic testing out there but up until then it was harder to
figure out which medications to start with and most physicians matter of fact I don’t know of
a single physician that actually starts out by saying well let’s do a genetic profile to see
what med to start you out with most we’ll start out with events as with a SSRI or some other
anti-anxiety medication some sort of a Benzo that’s been my experience so we may want
to encourage clients to consider genetic testing if they’re having difficulty finding a
medication regime that works for them and they are feeling like they have to have medication
genetic vulnerability also affects what’s going to make somebody more vulnerable now of all of you
in class today you know thinking about sleep you know sleep may not be a big deal for some of you
I know people who can go days or weeks with four or five hours of sleep and they feel fine it’s
not a big deal not me I need eight or nine hours of sleep so genetically for whatever reason I am
programmed to need a lot of sleep so when I don’t get that much sleep I tend to be it tends to be
harder for me to deal with life on life’s terms and I know that that makes me more vulnerable to
being irritable so genetic vulnerability affects who can become addicted affects what medications
work best and affects what situations are going to tend to make somebody more vulnerable to
anxiety so our medications and I know the type on here is small but we’re going to go through
it the first-line drugs are the SSRIs selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and the SNR is
selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors now the names are a little bit deceptive because
selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors also increase available serotonin but the mechanism
of action is different the mechanism of action for each SSRI is a little bit different as well
which is why you can put somebody on Prozac and they have an awful experience and you can put them
on zoloft and they have a much better experience like I said earlier a lot of the research pre
five years ago had been done on medications and zoloft paxil luvox lexapro celexa and their
generics have all been found to be effective at treating anxiety in certain people no one
medication works for everybody in the last five years effexor has come on the radar and it has
been a found effective according to the Hamilton rating scale for anxiety so that’s another one to
consider if clients are not successful or getting the treatment effect that they need for on some
of the other medications obviously none of us probably are prescribers but we do need to educate
clients about why the first drug or even the third drug that the doctor tries may not work so they
don’t start feeling helpless and hopeless like I said earlier there are at least four different
genetic variations which are correlated with the development of generalized anxiety disorder and
different medications are more or less effective depending on the genetic makeup of the person
there’s a high mortality rate moving on to two benzos the recommendation has actually switched
to really back off from the use of benzos now for some doctors will prescribe an SSRI and for the
first four weeks while the SSRI is building up in the system they will also prescribe a Benzo
to be taken as needed in order to moderate the anxiety and you know you could argue either side
of that if somebody has a history of substance use or substance dependence benzos are really
a bad idea because they do have a high rate of dependence but the other reasons that they are now
cautioning against the use of benzodiazepines is that there’s a higher mortality rate among benzo
users compared with non-users there’s an increased risk for dependence with use for more than six
months and that’s a long time to be using Benzo and when we’re talking about dependence and six
months we’re talking about somebody who uses it like every four hours or every eight hours
depending on your Benzo every single day, not a PRN user if somebody’s using it at night to
help them go to sleep or you know three or four times a week when the anxiety gets really high
the risk of dependence is relatively low but a lot of people with anxiety because if they find
the right Benzo it makes them feel so much better they may not want to be off of it and for a lot of
people when that benzo reaches its half-life and starts getting out of the system even more their
anxiety spikes you know they have rebound anxiety which they want to medicate with more benzos
that’s gonna be an issue for them to discuss with their doctor there’s also an increased risk
of dementia identified in long-term benzodiazepine users again this is for the people who use you
know throughout the day every day for six months or relatively every day for six months or more
and it doesn’t matter if it’s you know we’re talking about somebody who’s 65 or somebody
who’s 35 who’s been using Benzos for you know six months a year two years the risk of later
life dementia is greatly increased according to the research benzodiazepines also don’t treat
depression okay so if you’ve got somebody who has concurrent anxiety and depression there’s a much
higher suicide risk if they’re on benzodiazepines so being aware and generally that suicide risk
comes from overdosing on the benzodiazepines but not always other treatment options you know if the
benzos aren’t something that people want to touch you know they scare the living daylights out of
me and SSRIs and SNRIs don’t seem to be working then tricyclic antidepressants can be tried those
your older generation antidepressants seroquel is used a lot and there are some there’s some
research that shows it can be really effective with anxiety like some of the antidepressants and
depending on the person the benzos seroquel can make people very very very sleepy so you know
it may not the side effects of the seroquel the weight gain and the fatigue and you know
sleepiness may be unacceptable side effects for some clients and boosts perón is the third option
boost barone works more like an anti-depressive serotonin reuptake inhibitor and that it takes
you know four weeks or so to kind of build up in the system studies have shown that there’s really
no long-term benefit to taking it but six months to eighteen months of use it has been shown to
be effective in talking with clients a lot of clients report that boost bar when they take it it
doesn’t necessarily help them stop being anxious like a benzodiazepine does but it helps them not
go from zero to 200 in 2.3 seconds it kind of you know keeps them from having this gush of a freak
out reaction every time something goes wrong which a lot of clients report helps because they feel
more stable throughout the day after remission medication should be continued for six to twelve
months and during that last six months first six months keep it as is last six months you know
they say that tapering is best it’s best not to stop somebody cold turkey on any of these but
it’s definitely important for people once they’re in remission to not just suddenly go okay I feel
better I don’t need any of this anymore they need to work into it and make sure they’ve developed
the skills and tools that they need in order to deal with some of the anxiety that is going to
happen in life so physical signs and symptoms of anxiety may include fatigue irritability muscle
tension or muscle aches try laying feeling twitchy being easily startled trouble sleeping nausea
diarrhea irritable bowel syndrome headaches so the first thing we want to do with clients when we’re
talking to them well second thing first thing is say get a physical lets rule out physiological
causes of this but we can also help clients look at you know what might be causing these
things that you can do to mitigate it what might be contributing to your fatigue what might be
contributing to your irritability and your muscle tension or your muscle aches I mean let’s look at
economics did you recently get a new bed or do you need to get a new bed what about your desk chair I
know you know I get more muscle tension and muscle achy when I do a lot of mousing because I have
deplorable posture being becoming aware of that helps and then I’m like okay well I know it caused
it it’s unfortunate it’s unpleasant but it’s not a big deal trembling or feeling twitchy you know
that can be caused by low blood sugar that can be caused by anxiety that can also be caused
by early onset Parkinson’s symptoms you know there’s you know it can be worst case scenario
or it can be something really benign so we want to have people figure out you know when you start
trembling or feeling twitchy is there something that it’s related to you know I know when my
son gets really excited he’s he just sits there and you can see him almost shake because he’s so
excited about something so we want to have people prevent misidentification we don’t want them
to jump to that worst-case scenario we don’t want them to go onto WebMD and go oh my gosh I’ve
got cancer I’ve got this debilitating disease and I’m going to die in six months probabilistic Lee
speaking it’s not gonna happen yes get a doctor’s opinion I’m certainly not going to tell them it’s
all in your head I definitely want them to get an evaluation but I do want to in the meantime
help them really think about how likely is this and other things for headaches and this is
one another one of those that can be frustrating as we get older our eyesight starts to go and
you know there was a period there I did fine and then after I hit 45 my eyesight just started
to like steadily and kind of rapidly in my mind decline so I have to get my eyeglass prescription
changed every couple of years and that can cause headaches so instead of starting starting to worry
about oh my gosh I’ve got a headache all the time maybe I’ve got a brain tumor you know I know that
it’s it’s probably my glasses or I’m grinding my teeth so other biological interventions that
have been evaluated there’s something called the floatation rest system reduced environmental
stimulation therapy it reduces sensory input into the nervous system through the act of floating
supine which is on your back in a pool of water saturated with Epsom salt you know I’m looking at
this going that sounds really good and you can’t quite get the same experience in a bathtub because
you’re not floating you’ve got pressure points and you’re still hearing stuff clients can sort of
simulate it with you know earplugs or whatever but it’s if they can access this it’s been shown
to be really effective the float experience is calibrated so that sensory signals from visual
auditory olfactory gustatory thermal tactile or tactile vestibular gravitational and preceptive
channels are minimized that means you don’t see here taste touch smell feel nothing as is most
movement and speech so you want people to lay just like completely motionless and not talk which can
be hard for some people with anxiety in the study the study that I looked at fifty participants
reported significant reductions in stress muscle tension pain depression and negative effect and it
was accompanied by significant improvement in mood characterized by increases in relaxation happiness
and well-being I read the study I’m like where can I sign up you know it sounds in looking at some of
the research this was actually more effective for addressing anxiety than something like a massage
Tai Chi also produced significant reductions in anxiety there was approximately a 20% treatment
effect 25% treatment effect in patients with anxiety and fibromyalgia who practiced twice a
week for a year now you know we want to look at the con founding things here is it the Tai Chi
itself or is it learning to control the muscles and becoming more in tune with your body and
learning to control your breathing that helps people reduce their anxiety either way you know
Tai Chi helps people do that and it was shown that after a year after the first six months there was
a significant treatment effect but after a year you know it kept growing and after a year it was
about 25% so Tai Chi can be really effective an acupuncture at the HT 7 median Meridian can
attenuate anxiety-like behavior induced by withdrawal from chronic morphine treatment through
the meditation of the GABA a receptor system what does that mean that means if you if the
acupuncture is done in very certain places places the anxiety behavior the the GABA a receptor
system GABA is your main calming relaxation neurochemical that is triggered and it causes your
body to sort of flood that receptor system and this research was done on people who were detoxing
from morphine treatment but we can look at generalizing the results and I would be interested
to see further studies on it pain other things we need to do to help people with anxiety when people
are in chronic pain they often have anxiety that oh my gosh this is getting worse or iIt’snever
gonna get better or I just can’t take this pain anymore or they may get anxious that they’re going
to be rejected because they can’t do some of the things they used to do because they’re in so much
pain so there’s a lot of guilt and anxiety that can kind of revolve around pain what can we do
to help clients guided imagery is generally very helpful if we can help them imagine you know if
that pain in their shoulder imagine the pain is like the color red and flowing out of their arm
or other focus mindfulness so you know when you think about something you know when I get a shot
if I don’t think about it it doesn’t hurt near as much iasif the nurse says okay now one two three
and you know she’s counting down and I’m getting prepared and I’m really focused on it I had
another nurse one time who she was just talking to me and you know put the alcohol on my arm
and just kept on talking didn’t tell me she was getting ready to give me a shot and before I knew
it she had given me a shot and she was like okay we’re done I’m like you didn’t give me a shot yet
she said yes I did it’s like oh so not focusing on it and next time you have an itch for example
if you’ve ever been driving on the interstate and you can each on your on your foot I get those on
the bottom of my foot sometimes and I’m like okay I’m not going to pull over to each my foot if you
focus on something besides the itch eventually it goes away I’m not saying pain is gonna completely
go away but the more people focus on it the more it hurts physical therapy can help so encourage
them to get a referral and encourage them to do a self-evaluation if nothing else of ergonomics in
their car at work where they watch TV and spend most of their time at home and they’re sleeping
so those are the four places that they spend most of their time what do their ergonomics look like
and that can help for a lot of people mitigate a lot of pain hormones are another thing that
we need to look at imbalances of estrogen and testosterone can contribute to anxiety symptoms
heart palpitations fatigue irritability having people get a physical we can’t as clinicians do
anything about it but doctors can rapid heart weight rate sweating palpitations are not uncommon
in women in perimenopause or menopause so a lot of women start feeling like they’re developing
generalized anxiety and/or something’s going wrong when they start reaching that mid 40s to mid 50s
area and they start having some of these symptoms again we’re not going to diagnose it but we do
want them to recognize that it may not be anything you know catastrophic this is something that a
lot of women experience and help them figure out how to deal with that supportive care biologically
now you know this isn’t gonna treat anything but we can help them minimize their vulnerabilities
help them create a sleep routine so their brain and body can rebalance this can help repair any
adrenal issues that may be going on and improve energy level people with anxiety don’t sleep well
so helping them figure out how to get some quality sleep is important nutrition minimizing caffeine
and other stimulants is going to be a big help because those make people feel anxious encourage
them to work with a nutritionist to try to prevent spikes and drops in blood sugar which can trigger
the stress response when your blood sugar goes way up or way down you can start getting kind of shaky
and feel weird and that can cause people anxiety because they might think oh my gosh I’m having a
stroke or a heart attack or you know I don’t know what these tremors are so it’s important that
they don’t miss identify symptoms and encourage them to drink enough water dehydration can lead
to toxic Ardea which is increased heart rate sunlight vitamin D deficiency is implicated
in both depression and anxiety mood issues vitamin D has been found in those main areas where
serotonin receptors are found vitamin D receptors are found so we know the serotonin and vitamin D
have something going on sunlight prompts the skin to tell the brain to produce neurotransmitters and
set circadian rhythms which impact the release of serotonin your calming neurochemical melatonin
which is made from breaking down serotonin and it helps you sleep and gaba so sunlight actually
helps increase the release of gaba when it’s time to start calming down and going to sleep
exercise studies have shown that exercise can have a relaxing effect encourage clients to start
slowly there’s not a whole lot of new research on exercise and anxiety aromatherapy has been
used a lot in especially in other countries in the treatment of people with anxiety people with
hospital anxiety people women who are giving birth and they have some birth anxiety there they’ve
been found to be really effective in a lot of those studies essential oils for anxiety include
lavender rose Bedevere ylang ylang bergamot chamomile frankincense and Clary sage encourage
clients to just go to a health food store and you know sniff some of these see if it makes them
feel happy and calm and content the aromatherapy molecules enter the nasal membranes and they
will start triggering neurochemical reactions and so you don’t need to apply it you don’t need
to ingest it all you need to do is so encourage clients if they’re open to it to think about this
because aromatherapy can be integrated into their bedroom for example with an atomizer or a mr.
It
can be incorporated in a lot of different places again where they’re not applying it or ingesting
it in any way all they’re doing is smelling it they’ve used it in defusing aromatherapy in
hospital emergency rooms and they found that it reduces stress and irritability of the people in
emergency rooms and I’ve been to enough emergency rooms over the course of the years to know that
people who are in ers typically are not in the best mood so if it can help those people then
it’s probably going to have some sort of an effect so psychologically helping clients realize
that their body thinks there’s a threat for some reason that’s why it triggered the threat response
system which is what they call anxiety so they need to figure out why is there really a threat
you know sometimes it’s like the fire alarm going off in my house it just means that the windows are
open and there’s a strong breeze there is no fire there is no problem there’s just a malfunction
it’s a false alarm a lot of times for clients they get this threat reaction they get this stress
reaction and it’s not a big deal right now so they can start modifying what their brain responds to
and again those basic fears that a lot of people worry about failure rejection loss of control the
unknown and death and loss distress tolerance is one of those cognitive interventions that has
taken center stage in the anxiety research and it isn’t about controlling your anxiety you know
helping people recognize their anxiety acknowledge it and say okay I’m anxious it is what it is
how can I improve the next moment instead of saying I’m anxious I shouldn’t be anxious I hate
being anxious and slang with that anxiety let it go just accept it is what it is have the client
learn to start saying I am feeling anxious okay so distract don’t react because and I explain to them
the whole notion feelings come in crest and go out in about 20 minutes it’s like a wave so once they
acknowledge their feeling if they can distract themselves for twenty or thirty minutes you know
obviously they figured out there’s no real threat they if they can distract themselves for twenty or
thirty minutes those emotions can go down and then they can deal with it in their wise mind encourage
them to use distancing techniques instead of saying I am anxious or I am terrified or whatever
have them say I am having the thought that this is the worst thing in the world I am having the
thought that I cannot handle this because thoughts come and go and that comes from acceptance and
commitment therapy functional analysis makes it possible to specify where when with what frequency
with what intensity and under what circumstances the anxious response is triggered so it’s
important that we help clients develop the ability to do functional analyses on their own so
when they start feeling anxious they can stop and say okay where am I what’s going on how intense
is it what are the circumstances and they start really trying to figure out what causes this for
them so they can identify any common themes from their psychoeducation about cognitive distortions
and techniques to prevent those circumstances or mitigate them can be provided so if the client
knows that they get anxious before they go into a meeting with their boss and it’s usually a high
intensity of anxiety okay so we can educate them help them identify what fears that may be related
to techniques to slow their breathing and calm their stress reaction and help them figure out
times in the past when they’ve handled going in and talking to their boss and it really wasn’t
the end of the world you know there’s lots of different things we can do there for them there
but the first key and it gives them a lot of a huge sense of empowerment to start becoming
detectives in their own life and going okay now under what situations does this happen positive
writing this was another really cool study each day for 30 days the experimental group and this
was high school-aged youth in China but you know the experimental group engaged in 20 minutes of
writing about positive emotions they felt that day so they’re writing about anything positive
that make them happy that made them enthusiastic that gave them hope whatever long-term expressive
writing a positive emotions so after 30 days it appeared to help reduce test anxiety by helping
them develop insight and use positive emotion words so it got them out of the habit of using
the destruction and doom words and encouraged them to get in the habit of looking at the positive
things and being more optimistic it’s a really cool activity that clients can try it’s not gonna
hurt anything if you have them journal each day for 30 days mindfulness was also came up in the
research and was shown to be really effective in a meta-analysis six articles about mindfulness
based stress reduction four about mindfulness based cognitive therapy and three about fear of
negative appraisal and emotion regulation were reviewed all of these showed that mindfulness
was an effective strategy for the treatment of mood and anxiety disorders and is an effective
in therapy protocols with different structures including virtual modalities so you know if you’re
doing it via teleconference mindfulness can still be helpful mindfulness helps people start learning
how to observe what’s going on and become aware of what’s going on more aware of those circumstances
which will help them complete their functional analysis but it also helps them become aware of
vulnerabilities and head off things at the past and if they’re taking better care of themselves
that they’re living more mindfully then they may not experience as many situations that trigger
their anxiety mindfulness also encourages clients to learn acceptance that radical acceptance of
it is what it is I’m not gonna fight it I’m angry right now I am anxious right now however I’m
feeling right now is how I feel and that’s okay and it’s hard for clients to get to that but once
they get a hold of that and they truly believe it and they can say all right it’s fine I’m not gonna
feel this way forever I’m gonna do something else until the feeling passes it helps and that’s where
the labeling and letting go comes in mindfulness can also help them identify trigger thoughts
what thought were you having right before you started feeling anxious if people are mindful or
let’s start back when people are not mindful they often notice or don’t notice that they’re getting
anxious until they’re like super super anxious when people are mindful they become more aware of
subtle cues address unhelpful thoughts when they say or believe it’s a dire necessity for adults
to be loved by significant others for almost everything they do always running gonna happen
why is it a necessity what we can encourage them to do is concentrate on their own self-respect
on winning approval for practical purposes you know for promotions or whatever but it’s not about
me being lovable it’s about me getting a promotion and making more money and focusing on loving
rather than being loved because when we give love we generally get love back unhelpful thought
number two people feel they aren’t able to stand it if things are not the way they want them to be
or are not in their control so encourage clients to focus on the parts that are in their control
and other things in life which are going well and to which they’re committed number three misery
is invariably externally caused and is forced on us by outside people and events just reading
that makes me feel disempowered so encouraging clients to focus on the fact that reactions such
as misery or happiness are largely caused by the view that people take of the conditions so if
you see it as a tragedy and devastating then it’s probably going to produce misery if you
see it as an opportunity and a challenge it’s probably going to produce a different emotional
reaction if something is or may be dangerous or fearsome people should be terribly upset and
endlessly upset about obsess about it a lot of people with anxiety gets stuck on this you know
if I feel like its fearsome I need to worry about it getting on a plane for example if I fear that
that’s dangerous that I need to think about it and worry about it that’s not going to do any
good so encourage clients to figure out how to face it and render it harmless if possible and
when that’s not possible accept the inevitable so looking at airplanes you know facing it means
doing the research to figure out how dangerous is it really and realizing that it’s really not
that dangerous so that helps render it a little bit harmless in their mind it proves to them
that it’s not as dangerous as it could be and when it’s not possible to accept the inevitable you
know you got a fly so getting on there figuring out how you’re gonna get through it hurricanes
are the same way people especially in places like Texas Louisiana Florida may obsess as soon
as it starts coming to hurricane season or if a hurricane is spotted out in the Atlantic somewhere
they start checking the weather every hour or more wondering what the path is going to be and you
know what there’s you can’t change the path of the hurricane so all you can do is board up your house
evacuate if necessary and deal with the fallout child driving is just another example I’ll give
you know my children are learning how to drive and that’s kind of scary and fearsome you know what’s
gonna happen when they’re out there you know you see crashes all the time well render it harmless
by making sure they’ve got good training on how to drive make sure they’re good drivers and then
accepting that some things are just not within my control it’s easier to avoid than face life
difficulties and responsibilities Well running from fear is usually much harder in the long run
so encourage clients to look back at times when they’ve avoided difficulties and responsibilities
and the eventual outcome you know what happened there people believe they should be thoroughly
competent in achieving in all possible respects or they will be isolated rejected and failures we
need to encourage clients to accept themselves as imperfect with human limitations and flaws and
focus on what makes them loveable human beings what qualities like courage intelligence and
creativity and those things that can’t be taken away what inherent qualities do they have that
make them awesome people because something once strongly affected people’s lives they should
indefinitely fear it if you get lost you know when little kids get lost it’s terrifying when
you’re grown up if you get lost you turn on the GPS and you figure out your way but some people
still, you know freaked out about getting lost if they got lost once so we want to help people look
back at past episodes that may be contributing to the current anxiety and compare the situation’s
you know are you the same person or is this not a big deal now that you’re older wiser stronger
encourage them to learn from past experiences but not be overly attached to or prejudiced by
them yeah you could have maybe got lost in the past and it was a horrible experience well you
were six I can see where that would be terrifying and a horrible experience but it doesn’t have to
continue to impact you that way now when you’re you know 26 getting lost you know could be an
opportunity to try a new restaurant or something people must have complete control over things
well this doesn’t happen so encourage clients to remember that the past and the future are
uncontrollable we can’t change the past it is what it is we can learn from it so it doesn’t repeat
but we can’t change it and the future is largely uncontrollable I mean there are a lot of things I
can do to stay moving toward a rich and meaningful life but life is going to throw me curveballs
sometimes and there’s nothing I can do to plan for or control that we can control our actions in the
present to stay on our preferred path and develop general skills to deal with adversity
should it arise so we want to help clients develop those general problem-solving skills and
the general support system so when they are thrown a curveball you know it doesn’t knock them upside
the head people have virtually no control over their emotions and cannot help feeling disturbed
by things well encourage them to think about the fact that they have real control over destructive
emotions if they choose to work at improving the next moment and changing inaccurate thoughts then
they’re not going to experience the destructive emotions as intensely or as frequently when you
feel an emotion you feel how you feel but again you don’t have to wrestle with it fight it and
nurture it you can say this is how I feel how do I improve the next moment when it comes to
cognitive distortions encourage them to find alternatives when they start to personalize things
if somebody laughs when you walk out of the room then the person starts getting anxious
thinking oh they were making fun of me I wonder what they thought I wonder if I had something
stuck to the back of my dress and they start getting all panicked about it that doesn’t do
any good encouraging them to think you know what our three alternate explanations that hadn’t but
had nothing to do with you for why they laughed magnification of the worst thing you know taking
something and saying if this happens then it’s going to be a catastrophe and minimisation going
along with that a lot of times when people magnify and see a catastrophe they minimize not only
their own strengths and resources but all the other stuff that they’ve got going for them all
they’re seeing is this catastrophe so encouraging them to focus on the facts what is actually
happening and what is the high probability event and and encourage them to get information
and look at the broader picture you know yes you got into a car crash and your car is totaled and
that is unfortunate you know it really sucks but you know that is not going to cause you to lose
your job and then become homeless and penniless and yadda-yadda it might cause your insurance to
go up but okay so you don’t have a car but what are the resources that you have who can who do
you work with that might be able to give you a ride to work you know let’s look at the resources
you have and work around so problem-solving helps with magnification and also focusing on you know
let’s be grateful for what didn’t happen you know you could have been killed but you weren’t the
car was totaled it’s replaceable all or nothing thinking again have them think about what else
could have been happening like Brittney suggested finding the exceptions instead of saying she
always does this look for exceptions when has she not done that what else has she done instead
of this selective abstraction and filtering is when people look for the good the bad and the
ugly a selective abstraction means you kind of see what you expect to see so if you expect
something to be devastating you see only the devastating aspects of it which kind of goes with
the magnification and minimization you filter out the stuff a lot of times when people are in a bad
mood or are anxious they see the negative because that’s the state of mind they’re in so encourage
people to complete the picture alright there’s all this bad stuff now what’s the good stuff you
know encourage them to look at the good the bad and the ugly so they get a wide view of exactly
what’s going on and encourage them to remember that hindsight is twenty-twenty when people have
something embarrassing happen or they get anxious about something that that happened they look back
and they go I should have or I could have or Oh I wish I wouldn’t have when you were in that
situation you did what you did and you know maybe you may have had a reason for it or you know
you may have not had other options or it may have just been a bonehead thing to do but okay so you
made one mistake hindsight is 2020 that’s gonna that mistake is gonna stand out just like the
great big letter on the eye chart because you’re thinking back and you’re looking at it and that’s
all you see but encouraging clients to remember that other people are too busy worrying about
themselves to really remember what you did jumping to conclusions encourage clients to remember to
get all the data if your significant other male significant other comes home and is smelling like
perfume don’t just jump to the conclusion that he was cheating on you maybe he went to the to the
mall to get a new tie and walked through the perfume area and got spritzed or bought you some
perfume or who knows maybe the person sitting next to him at work sprayed her perfume at the desk
and some of it filtered on there’s all different reasons that that might happen so encourage people
to get all the data mind reading we can’t do it you know you can’t read somebody’s mind you don’t
know what they’re thinking so ask them if you what do you think about this don’t assume anything and
emotional reasoning encourage people to step back from a situation and ask themselves am i feeling
anxious about this because I’m feeling anxious and I’m looking for reasons that it should be scary
or am i feeling anxious about this because it’s really scary for some reason there’s actual facts
support my anxiety a lot of times when we go into new situations we may feel anxious because it’s
a new situation but when we step back we say you know what there’s really nothing to be worried
about here you know no big deal I got this and move on so instead of rolling with it and trying
to figure out okay I feel anxious so there must be a reason not necessarily very likely a false
alarm other psychological interventions relaxation skills encourage people to learn how to relax
not only physically but mentally diaphragmatic breathing is helpful encouraging them to breathe
through their stomach and put their hand on their belly and feel their belly expand and contract
slows breathing down which triggers the rest and digestion reaction in the brain which is calming
meditation can be helpful for some people some people find trying to quiet their mind too
frustrating because they’ve got too much monkey mind going on that can be later or maybe
never for some people we don’t want to increase their anxiety with interventions cute progressive
muscular relaxation also has a lot of research support and remember with cute progressive
muscular relaxation we’re Sakura geing them to attach a cue AK you word like relax or breathe
with the relaxation response so they tense their muscles and then they relax their muscles and as
they relax their muscles they say their q”-word like relaxed and they work from head to toe or
from toe to head tensing and relaxing different muscle groups so they become more aware of what a
tense muscle feels like versus a reactive relaxed muscle there are great scripts that are online
that people have already recorded that can walk people walk clients through CPM are I highly
encourage it because once they get used to it then they can just think that cue they can think
relax and as they exhale they will start to feel their entire body kind of relaxing because it’s
trained when it hears that just like when you hear the word pop quiz when you were in high school
you had a stress reaction well we want to use it in reverse and train train the body so when
it hears a cue word it relaxes help them develop self-esteem because fear of failure and rejection
a lot of times come from needing other people’s approval help them develop a rational idea of
their real self develop compassion self-talk instead of saying I’m an idiot or I’m stupid or
I’ll never measure up to anything encourage them to talk to themself like they would talk to their
child or hopefully their best friend and encourage them to spotlight strengths whenever they feel
like they’ve got an imperfection to identify these three strengths that they have so they’re you know
balancing out the imperfections and the strengths of cognitive restructuring reframe challenges in
terms of current strengths, not past weaknesses so if you’re going to give a presentation in front
of 60 people and you hate public speaking instead of thinking about you know this is terrifying
because the last time I went up in front of people I forgot everything I was going to say and drop
my note cards well that’s a past weakness what is your current strength you’re prepared you know
the material you yadda-yadda so encourage people to look at all the strengths and resources they
currently have them develop an attitude of gratitude and optimism because like I said with
that the positive writing exercise when people are in a grateful optimistic frame of mind they
tend to see more of the good stuff they see the bad stuff too but they can also see more of the
good stuff and some of the bad stuff they see opportunistically instead of as a devastation
acceptance and commitment therapy says that some of the reasons that we’re miserable is
fear we get fused with our thoughts we think I am terrified well if I am terrified then I can’t
I mean if I am I can’t get rid of anything I am if II havethe thought that I’m terrified
well I can get rid of a thought I can forget things easily encourage people to evaluate their
experience and empower them to look at things as challenges and opportunities instead of hardships
encourage them not to avoid their experiences so things that are scary gradual exposure and
finding exceptions like for me bridges you know I love public speaking so that’s not a
thing but when I go to a bridge you know when I Drive to the bridge you know when I’m on the
bridge somebody else is driving I get used to doing that when I Drive over a bridge then when
I Drive over one of those bridges that opens up I hate those bridges um I know y’all are just like
oh my gosh yeah it’s an irrational fear I realize that but instead of going straight for the bridge
that opens up going for the little bridges first and then thinking back over times that I’ve gone
over bridges and there’s been no problem you know there are exceptions nothing happened it wasn’t a
big deal Sometimes I didn’t even notice it until somebody pointed out hey look down there at that
pretty water and I’m like oh we’re on a bridge so encourage people to not avoid their experiences
get used to them embrace them and learn that they have the power to deal with them and stop reason
giving for behavior you know use the challenging questions if something is fearsome let’s look for
at the evidence for and against it instead of you know making excuses for social interventions
improve their relationship with themselves self which goes with self-esteem improvement people are going
to feel less anxious about getting their needs and wants met if they know what their needs and wants
are so part of that is becoming mindful cuz a lot of our clients don’t know what they need and want
they just want to feel better but they don’t know how they don’t know what they need to feel
better so helping them identify their needs and wants and encourage them to be their own best friend
you know when they get a promotion take themselves out to dinner pat themselves on the back whatever
it is don’t rely on other people to do it because other people it’s not that they don’t care but
other people are often very involved in thinking about their stuff and they may not notice
encourage them to develop a method of internal validation so they can feel like they are all
that ‘no bag of chips and they realize why they are lovable human beings and they accept the
the act that everybody is not going to like them and nobody is gonna like them all the time and
that’s okay you know my kids don’t like me all the time my husband doesn’t like me all the time
I’m okay with that I know I can be challenging but you know most of the time you know they like me
and and that’s okay and there are some people you know who don’t like me at all and okay there’s
nothing I can do about that helping our clients develop aanokayness with that helps relieve a lot
of anxiety because a lot of people feel like they have to be liked by everybody and if somebody
doesn’t like them it’s like what did I do wrong oh my gosh encourage them to develop healthy
supportive relationships with good boundaries develop assertiveness skills so they can ask for
help when they need it anxiety a lot of times you know that’s the body saying there’s a threat well
if there’s a threat maybe you need some help you know dealing with it so people need to be willing
and able to ask for help and not feel like that’s going to lead them to be rejected and allow them a
certif this will allow them to say no to requests again without feeling like that’s going to result
in them being fully rejected describe the ideal healthy supportive relationship and encourage
them to separate the ideals from the real you know let’s look at if you had a best relationship
what would it look like okay you know Warden June Cleaver we got that now how realistic is that
you know let’s look at you know rephrasing this a little bit so it’s less extreme you know warden
June Cleaver never fought their kids were perfect you know all those extreme words let’s look at
what’s real what happens in real relationships encourage people to identify who would be
a good partner in supportive relationships I’m not meaning necessarily romantic I’m meaning
friends and where they can be found you know where would you find people that you could be friends
with and encourage them to play though what does it mean when game cuz a lot of times again this
goes with mine reading you know what does it mean when your friend doesn’t return your text right
away what does it mean when your friend cancels dinner on Friday night what does it mean when
you see where I’m going with this and a lot of times clients with anxiety and rejection issues
and low self-esteem will go to the worst-case scenario so encourage them to go back to finding
the exceptions what else could have been happening what else could it be that caused this and it’s
not about you so anxiety is a natural emotion that serves a survival function excessive anxiety can
develop from lack of sleep nutritional problems neurochemical imbalances failure to develop
adequate coping skills cognitive distortions low self-esteem and a variety of other stuff recovery
Ambala involves improving health behaviors making sure your body’s functioning and making the
neurotransmitters it needs and you know release them as needed to identify and build on current
coping strategies address cognitive distortions and develop a healthy supportive relationship with
self and others if you enjoy this podcast please like and subscribe either in your podcast player
or on YouTube, you can attend and participate in our live webinars with Dr.
Snipes by subscribing
at all CEUs comm slash counselor toolbox this episode has been brought to you in part by all
CEUs calm providing 24/7 multimedia continuing education and pre certification training to
counselors therapists and nurses since 2006 used coupon code consular toolbox to get
a 20% discount off your order this month.
My 6-step formula for GCSE exam success. Achieve a top grade in all your GCSE exams whilst spending half of your time doing the things you enjoy. I explain why note-taking is NOT the way ➯➱ ➫ ➪➬ The General Certificate of Secondary Education (GCSE) is an academic qualification in a particular subject, taken in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland. State schools in Scotland use the Scottish Qualifications Certificate instead. Private schools in Scotland may choose to use GCSEs from England.